Photonic Crystal Fiber
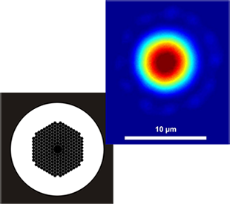
KONGTUM Technology can provide a variety of different types of photonic crystal fibers to meet the different application needs of users. It can also customize a variety of fiber optic jumpers with different connectors, or perform special processing according to user needs.
The photon belt gap (hollow core) optical fiber conducts light in the gap surrounded by the microstructure cladding. The photon belt gap can be formed in a material with a periodic structural refractive index, such as in quartz by periodically arranging air holes. The photon belt gap in the cladding is equivalent to a nearly lossless reflector, limiting light to the core, which does not need to be made of solid materials. For some types of PCF, less than 1% of optical power will propagate in the glass, significantly reducing the impand negligible interface reflection. In addition, it is also possible to produce low loss optical fibers using relatively high loss materials, expanding the range of materials that can be used to manufacture optical fibers. The optical fiber is protected by a single layer of acrylic coating, which can be peeled and cut like ordinary solid optical fibers.
It can be applied to transmit high-power broadband radiation in a spatial mode, ultrashort high-power optical pulse transmission, pulse compression and pulse shaping, mode filtering, multi wavelength guidance, laser pigtail, sensors and spectroscopy, interferometer and other fields.act of glass materials on fiber properties. Therefore, hollow PCFs exhibit extremely low nonlinearity, high breakdown threshold, zero dispersion at the design wavelength,
Parameters
The following are some fiber optic parameters. For more information on fiber optic products, please consult sales personnel!
HC-1550-02 Parameter | |
Fiber core/cladding/coating diameter | 10±1um / 120±2um / 220±30µm |
PCF area diameter | 70±5µm |
Wavelength | 1550nm |
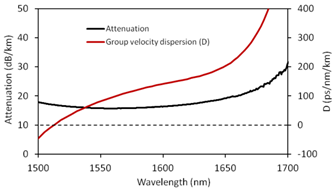
Attenuation | <30dB/km @ 1550nm |
GVD | 90ps/nm/km @ 1550nm |
Working wavelength (attenuation<0.25dB/m) | 1490-1680nm |
MFD | 9±1µm @ 1550nm |
NA | ~0.20 |
Typical attenuation and dispersion curves |
|
Features
Wavelength 800, 1060, 1550, or 2000 nm
7-core provides large continuous working bandwidth
Low number of central and parasitic surface modes
Zero dispersion at design wavelength
Near Gaussian distribution fundamental mode
Almost no optical nonlinearity
Almost no bending loss
No Fresnel reflection on the end face (mode refractive index ≈ 1)
Capable of welding, punching, and other processing according to application requirements